干货满满|A-level经济学通货膨胀的原因及后果
2020-03-17 环球教育
Two Broad Causes of Inflation

A: cost-push inflation: the rise in the price of imports will increase import prices and this might increase input costs leading to cost-push inflation.
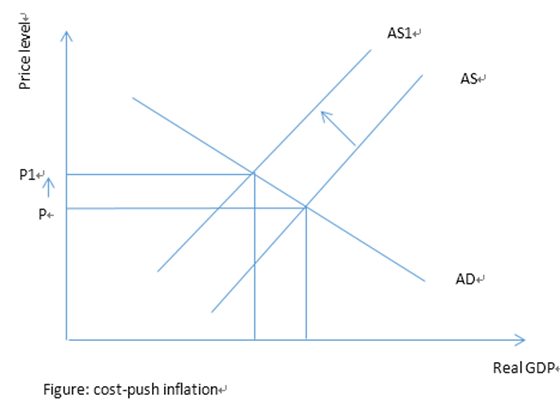
B: demand-pull inflation: a fall in the exchange rate will lead to a fall in the price of exports and a rise in the price of imports, this will lead to a rise in net exports and this will increase aggregate demand that could result in inflation.
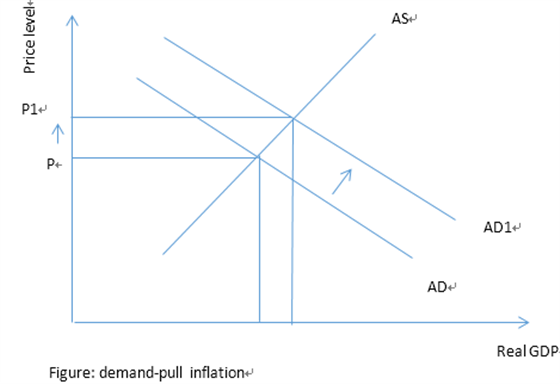
Alevel 真题干货满满,为大家备考充电!
1. (June, 201721)
4 (a) Explain how a fall in an economy’s foreign exchange rate can cause both cost-push and demand-pull inflation. [8]
Solution:
1) 答题思路:根据题目可分成两部分回答:cost-push inflation and demand-pull inflation 的定义;分别阐述a fall in exchange rate 如何产生 cost-push inflation 和demand-pull inflation.
2) 得分点:
For knowledge and understanding
• of demand-pull inflation (up to 3 marks)
• and cost-push inflation (up to 3 marks)
(4 marks maximum)
For application
• showing how a deadline in an economy's exchange rate can cause cost-push inflation (up to 3 marks)
• demand-pull inflation (up to 3 marks)
(4 marks maximum)
3) 真题答案:
A fall in the exchange rate will lead to a fall in the price of exports and a rise in the price of imports. this will lead to a rise in net exports and this will increase aggregate demand that could result in inflation.
This rise in the price of imports will increase import prices and this might increase input costs leading to cost-push inflation.
2. (November, 2012v1)
3 (a) Explain, with the use of an aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply(AS) diagram, the different effect of cost-push and demand-pull inflation on real output. [8]
Solution:
1) 答题思路:解释cost-push inflation和demand-pull inflation的定义,再分别画ADAS的图解释cost-push inflation和demand-pull inflation对real output的影响。
2) 得分点:
For knowledge and understanding of cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation and real output (Max, of 2 for anyone) [4]
For an analysis of the effects on real output. [4]
3) 真题答案:
Inflation is a persistent rise in the general price level. Cost- push is based on rising costs such as wages, raw materials, taxes and affects the AS curve. Demand-pull results when consumption, investment, government spending or exports minus imports shift the AD curve.
A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve on an upward-sloping section of the aggregate supply curve will cause inflation and Increase real output. A shift to the left of the aggregate supply curve will also cause inflation but will reduce real output.
3. (June, 2014v2)
4 (a) Using diagrams, explain the difference between demand-pull and cost-push causes of inflation. [8]
Solution:
1) 答题思路:根据题目分成两部分写:cost-push inflation和demand-pull inflation的定义;分别画ADAS图解释两者间的区别。
2) 得分点:
For knowledge and understanding of demand-pull and cost-push causes of inflation (up to 4 marks)
For application using appropriate diagrams to distinguish between the two types of inflation (up to 4 marks)
3) 真题答案:
For stating that demand-pull inflation is caused by an increase in aggregate demand (1).
For explaining the possible cause of an increase in aggregate demand such as an increase in consumption, investment, government expenditure or net exports (1).
For stating that cost push inflation is caused by an increase in costs (1).
For explaining the possible cause of an increase in costs such as an increase in wage rates, raw materials etc. (1).
Diagrams showing how exchanges in aggregate supply and aggregate demand may lead to inflation.
Award marks for diagrams as follows:
• A ‘micro’ diagram should be awarded 0 marks.
• A ‘macro’ diagram that is not fully accurate may gain 1 mark.
• An accurate ‘macro’ diagram is require for 2 marks.
One accurate diagram showing both demand pull (AD) and cost push (AS) causes could gain 4 marks (8 marks total).
The Consequences of Inflation
A: Internal consequences
1) menu costs: costs to firms of having to change prices due to inflation.
2) Shoe leather costs: costs of moving money around in search of the highest interest rate.
3) Redistributive effects: Inflation reduces the purchasing power of people who live on fixed incomes, and will reduce their living standards. It redistributes national income from the poor to the well-off since the former have fewer choices to hedge against inflation.
4) Less saving: Inflation discourages saving & there will be fewer savings available in the economy for investment. Borrowers gain at the expense of lenders and savers.
Greater uncertainty: Inflation increases uncertainty in business decision-making as firms find it hard to judge whether an investment prospect will or will not be profitable. As a result investment will fall, and in the long run, growth and employment rates may decline.
B: External consequences
1) Damage to export competitiveness: If a country’ inflation rate is higher than its competitors’, this may cause exports to fall. This will have an adverse effect on the balance of payments & the export sector.
2) Reduce the burden of debt: real interest rates may fall due to inflation or may even become negative. This is because nominal interest rates do not tend to rise in line with inflation. As a result, debt burdens may fall.
继续充电...
1. (June, 2014v2)
(b) Distinguish between the domestic and external consequences of inflation and discuss which is most damaging to an economy. [12]
Solution:
1) 答题思路:问题分成两部分回答,第一部分回答consequences of inflation:把consequences of inflation分成external 和internal。第二部分写自己的观点认为哪个consequence is most damaging to an economy并写出原因。
2) 得分点:
For an analysis of the internal and the external consequences
(up to 8 marks).
For evaluative comment on “the most damaging” element of the question (up to 4 marks).
3)真题答案:
The analysis must make clear the distinction between the internal and external consequences of inflation. The analysis must also explain the consequences of each. Internal consequences include the impact on savings and investment, the re-distribution of income, menu costs and shoe-leather costs. External consequences include the impact on trade and the exchange rate and international investment flows. For full marks for evaluation, a conclusion must be provided.
(Allow up to 6 marks if only the internal or external are considered).
If the candidate explains the consequences of inflation but fails to distinguish between internal and external, then a maximum of 6 marks may be awarded.
Relevant evaluative comment, might include the extent to which an economy engages in trade, whether an economy has a fixed, floating or managed floating exchange rate and so on.
更多干货请关注:http://beijing.gedu.org/ 干货满满专栏为您持续更新!


1 环球教育培训学校2025寒假雅思课程全面升级,助力突破语言瓶颈
2 环球教育三维动态教学体系精准应对雅思改革,2025寒假班助力考生冲刺高分
3 环球教育雅思培训:三维动态教学体系引领留学备考新风尚
4 环球教育多维创新引领语言培训,28年深耕构建国际教育生态圈
5 环球教育培训机构 2025 年度成果发布,全品类服务覆盖学子成长全周期
6 环球教育雅思班全新升级,三维动态教学体系精准应对机考改革
7 环球学校雅思培训:三维动态教学体系助力学子精准提分
8 雅思6分相当于英语几级?国内英语等级对照全解析
9 环球教育雅思培训再添高分案例,28 年深耕铸就提分标杆
10 环球教育培训学校:以多元课程与匠心服务,点亮学子成长之路
北京市海淀区环球雅思培训学校 版权所有 课程咨询热线:400-616-8800
Copyright 1997 – 2025 gedu.org. All Rights Reserved 京ICP备10036718号
全部课程、服务及教材面向18岁以上人群
市场合作申请